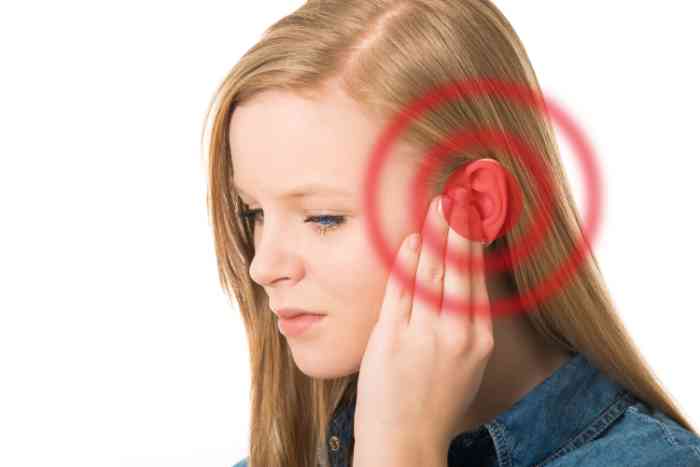
Cauliflower ear is a condition where fluid collects between the ear’s skin and cartilage, causing swelling and damage. Without treatment, cauliflower ear can cause the ear to become permanently thickened and misshapen, while also leading to discomfort and an increased risk of infection.
What is a cauliflower ear?
Cauliflower ear is a deformity of the outer ear that occurs after repeated trauma or friction, commonly seen in combat and contact sports. The cauliflower ear medical term is auricular hematoma, which describes the buildup of blood between the skin and cartilage. This disrupts normal ear anatomy, preventing proper blood flow and leading to cartilage death and thickening. Over time, the ear hardens and becomes permanently misshapen.
Cauliflower ear symptoms: what does it look like?
Stage 1: start of cauliflower ear
Stage 2: progression and bruising
Stage 3: hardening and deformation
Stage 4: burst and worst cauliflower ear


Does a cauliflower ear affect hearing?
Cauliflower ear generally does not affect hearing because the damage occurs mainly to the outer ear’s cartilage, which doesn’t play a direct role in the hearing process. The condition changes the ear’s shape and appearance but usually doesn’t interfere with the ear canal or the inner structures responsible for hearing. However, in severe cases where swelling or deformity blocks the ear canal, it might cause some temporary hearing difficulties or discomfort.
How to get cauliflower ear: causes
Why do wrestlers get cauliflower ear?
Does it hurt getting punched with cauliflower ear?
Is cauliflower ear dangerous and contagious?
Cauliflower ear is generally not dangerous and is not contagious, but can lead to complications if left untreated. The main concern is that the accumulated fluid can cause pressure on the ear’s cartilage, leading to permanent deformity. Additionally, if the ear becomes infected, it can result in pain, swelling, and more serious infections that require medical treatment. In rare cases, untreated infections could spread or cause lasting damage.
While cauliflower ear itself is mostly a cosmetic issue, prompt treatment is important to avoid discomfort, infection, and irreversible changes to the ear’s shape.
Treatment options of cauliflower ear
Draining cauliflower ear
Plastic surgery
Antibiotics


How long does it take to get cauliflower ear?
Cauliflower ear usually appears within 7 to 10 days following an injury, particularly when treatment is delayed. The blood trapped under the skin can solidify within one to two days, making it harder to drain. Sometimes, people may experience a sudden release or ear pop when the fluid bursts, but attempting this without medical help can lead to infection or further damage. Without timely care, this hardened buildup can cause lasting changes to the ear’s shape.
Does cauliflower ear go away or is permanent?
Cauliflower ear does not typically go away on its own and is usually permanent if left untreated. While early treatment — such as draining the fluid and preventing infection — can help prevent permanent damage, once the scar tissue has formed and the ear has changed shape, the deformity tends to remain. In some cases, surgical procedures may improve the appearance, but complete reversal is often difficult. Therefore, prompt care is important to avoid permanent cauliflower ear.
How to prevent and avoid cauliflower ear
Preventing and avoiding cauliflower ear primarily involve wearing ear protection, especially in contact sports like wrestling, boxing, and rugby where ear injuries are common. Wearing protective headgear or ear guards can significantly reduce the risk of injury by cushioning the ear against blows and friction. Some athletes also use BJJ (Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu) cauliflower ear magnets as a complementary method to help reduce swelling and promote healing, although scientific evidence on their effectiveness is limited.
It’s also important to address any ear injuries promptly — if swelling or a hematoma develops, immediate medical attention to drain the fluid and apply compression can prevent the formation of scar tissue. Maintaining good hygiene and monitoring for signs of infection can also help prevent complications.
How to diagnose a cauliflower ear
Newborn with cauliflower ear
Famous cases of cauliflower ear
Several famous personalities are known for their distinctive cauliflower ears, often linked to their involvement in combat sports or physical roles.
- Mike Tyson, the legendary boxer, is one of the most iconic examples, with his cauliflower ears reflecting years of intense fights in the ring.
- Adam Sandler, an actor who trained in boxing for various movie roles, has also been seen with noticeable cauliflower ears, showing the physical toll of his training.
- More recently, UFC fighter Adrian Yanez has gained attention not just for his striking skills but also for his prominent cauliflower ears, a common trait among mixed martial artists due to repeated ear trauma.
These well-known figures highlight how cauliflower ear is often a badge of honor in combat sports and physically demanding careers.
Living with cauliflower ear
Living with cauliflower ear means adapting to a permanent change in the shape and appearance of the ear, which can sometimes affect self-confidence or comfort. While the condition itself is usually painless once healed, the thickened and swollen ear may be more prone to infections or irritation if not cared for properly.
People with cauliflower ear often take extra precautions to protect their ears during physical activities to prevent further damage. For some, the ear’s unique look becomes a symbol of resilience and dedication, especially among athletes and fighters who see it as a badge of honor earned through hard work and perseverance.
FAQs about cauliflower ears
Can you wear airpods with cauliflower ear?
Can cauliflower ear be genetic?
Can you get cauliflower ear from sleeping on side?
With you on your journey to better hearing.
It's time to finally treat your hearing loss. Sign up for a free consultation with a licensed hearing care professional today to determine if you have hearing loss. It’s the start of your journey towards better hearing.
EarPros benefits:
- it's 100% risk free.
- best partner with more than 1.000 stores