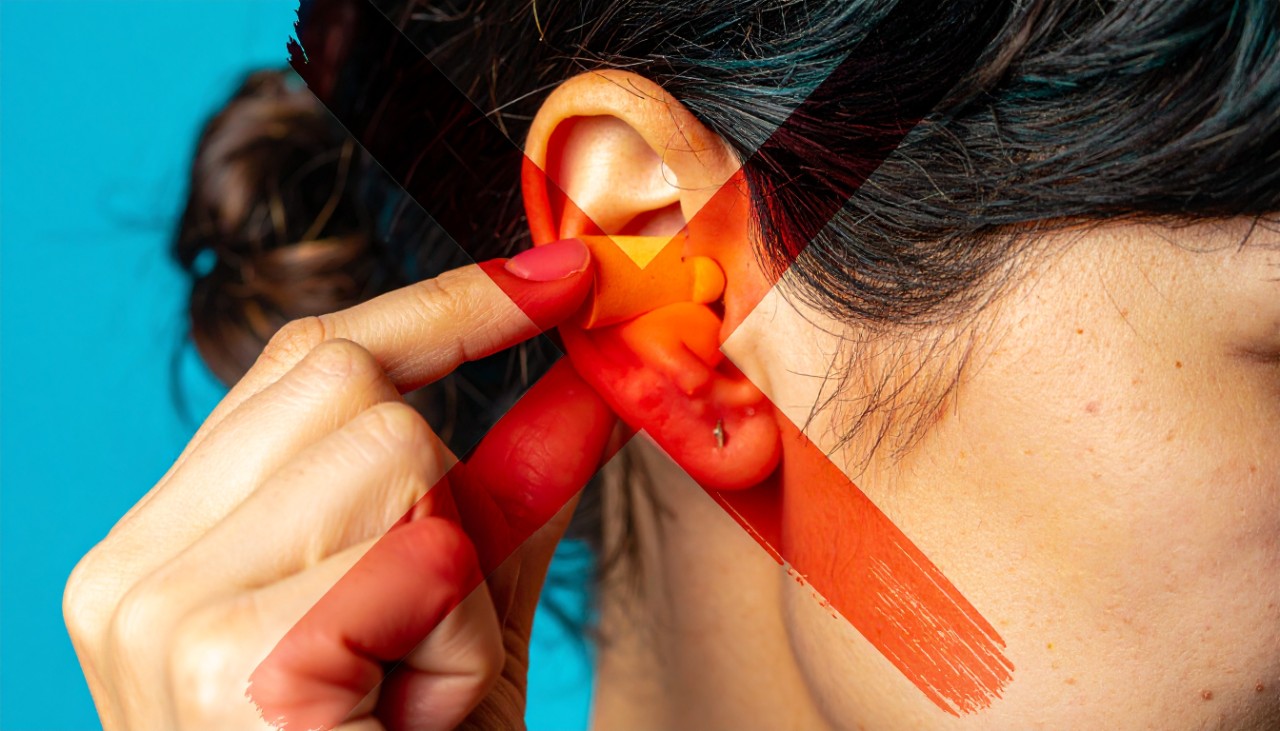
Ear bleeding and otorrhagia: causes, symptoms, and remedies
Unexplained otorrhagia is a symptom that requires immediate attention, it often occurs with or without pain. Regardless, it needs to be observed critically as it may indicate a larger, underlying condition. Bleeding from the ear might also manifest as blood in the ear wax, as opposed to overt bleeding.
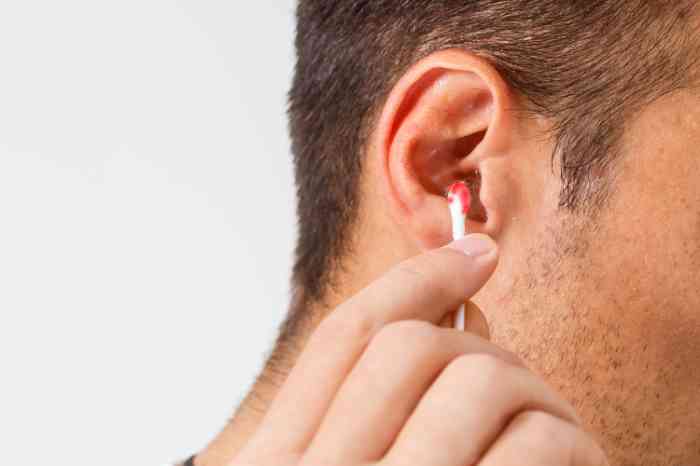
Many factors can lead to ear bleeding, shockingly even common practices like improper use of cotton swabs or Q-Tips. Severe causes include head injuries or acoustic trauma which may damage or rupture your eardrum accompanied by extreme pain.
Ear bleeding with no pain


Why is my ear bleeding?
While otorrhagia often suggests a perforated eardrum due to infections or ear trauma, here are some other common factors leading to ear drainage:
1. Improper cleaning and blood on Q-tip after cleaning ears
Many individuals often overlook the risks of regularly using cotton swabs or Q-Tips for ear cleaning. The persistent scraping against the delicate walls of the ear canal can cause abrasions or, in more severe instances, puncture the eardrum. The absence of pain does not necessarily indicate that there is no damage. If you notice blood on Q-tip after cleaning your ears with a cotton bud, or if there is blood present on the Q-tip mixed with earwax, it could be a sign of an injury within the ear canal. It's crucial to be gentle when cleaning your ears and to avoid inserting any objects deep into the ear canal to prevent such injuries.


Otitis media, which encompasses both acute and chronic forms of ear infections, is a notable cause of ear bleeding. These infections can result in the accumulation of pus and fluid in the middle ear, leading to increased pressure that may cause the eardrum to rupture, resulting in discharge that can include blood. In instances of persistent purulent middle ear infections, medical intervention may be necessary. This often involves the insertion of tympanostomy tubes, also known as pressure equalization (PE) tubes, which serve to ventilate the middle ear and prevent the build-up of fluids.
Additionally, a specific type of ear infection called myringitis can also lead to ear bleeding. Myringitis is characterized by inflammation of the eardrum, and in some cases, blisters on the tympanic membrane can form and subsequently burst, which may result in bleeding. This condition can be particularly painful and may require prompt medical treatment to alleviate symptoms and address the infection.
3. Foreign objects and bleeding ears risks
In addition to the misuse of Q-Tips, ear bleeding can also result from the insertion of foreign objects into the ear, which is a common issue among children. Youngsters often insert small items into their ears out of curiosity, which can cause similar or more severe injuries than those caused by cotton swabs. Otorrhagia from misuse or foreign objects should be taken seriously, and medical advice should be sought to ensure that there is no significant injury or risk of infection.
It's crucial to educate both adults and children on the proper care for their ears and the dangers of inserting any objects into the ear canal. Gentle cleaning practices and supervision of children during their cleaning routines can help prevent these common yet avoidable causes of otorrhagia.
4. Minor injuries: bleeding eardrum
Minor injuries to the ear, such as small abrasions or slight trauma to the ear canal or eardrum, can result in a bleeding eardrum, though typically the bleeding is not excessive. Such injuries might occur from everyday activities like vigorous ear cleaning, the insertion of earbuds, or even an abrupt change in air pressure. While the sight of blood can be alarming, these minor injuries often resolve on their own without the need for medical intervention, as the tissues within the ear have a good capacity for self-repair.
Less frequent cases for ear bleeding
Barotrauma and otorrhagia
Bleeding from the ear after head injury
Ear bleeding and high blood pressure
Otorrhagia is not commonly associated directly with high blood pressure; however, the two may have an indirect relationship. High blood pressure, or hypertension, can lead to various complications that might increase the risk of conditions that could cause ear bleeding.
For instance, hypertension can contribute to blood vessel damage or create conditions for blood vessel rupture, which, in rare cases, might affect the vessels in the ear, especially if there is an existing vascular abnormality within the ear itself.
Additionally, high blood pressure is a risk factor for cardiovascular events that could potentially lead to head injuries or falls, which in turn might result in ear trauma and subsequent bleeding. It's also worth noting that the stress of experiencing ear bleeding could temporarily elevate blood pressure due to anxiety.
If you are experiencing ear bleeding and have known high blood pressure, it is important to monitor your blood pressure and seek medical attention to address both the ear bleeding and to ensure your hypertension is well-managed to prevent further health issues.
Cancer of the ear canal: bleeding from the ears
Cancer of the ear canal, though relatively rare, is a serious condition that can manifest with several symptoms, one of which may include bleeding from the ears.
This bleeding is typically a result of the tumor disrupting the normal structure and function of the ear canal and potentially invading the surrounding blood vessels. As the cancerous cells grow, they can erode the delicate tissues within the ear, leading to ulceration and bleeding.
This symptom, especially when accompanied by other signs such as persistent ear pain, hearing loss, or the presence of a mass or lump in the ear canal, should prompt immediate medical evaluation.
An otolaryngologist, a specialist in ear, nose, and throat disorders, can perform a thorough examination, which may include imaging and a biopsy to determine the presence and extent of the cancer. Treatment for ear canal cancer typically involves a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, depending on the stage and aggressiveness of the tumor. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving the prognosis and managing the symptoms effectively.


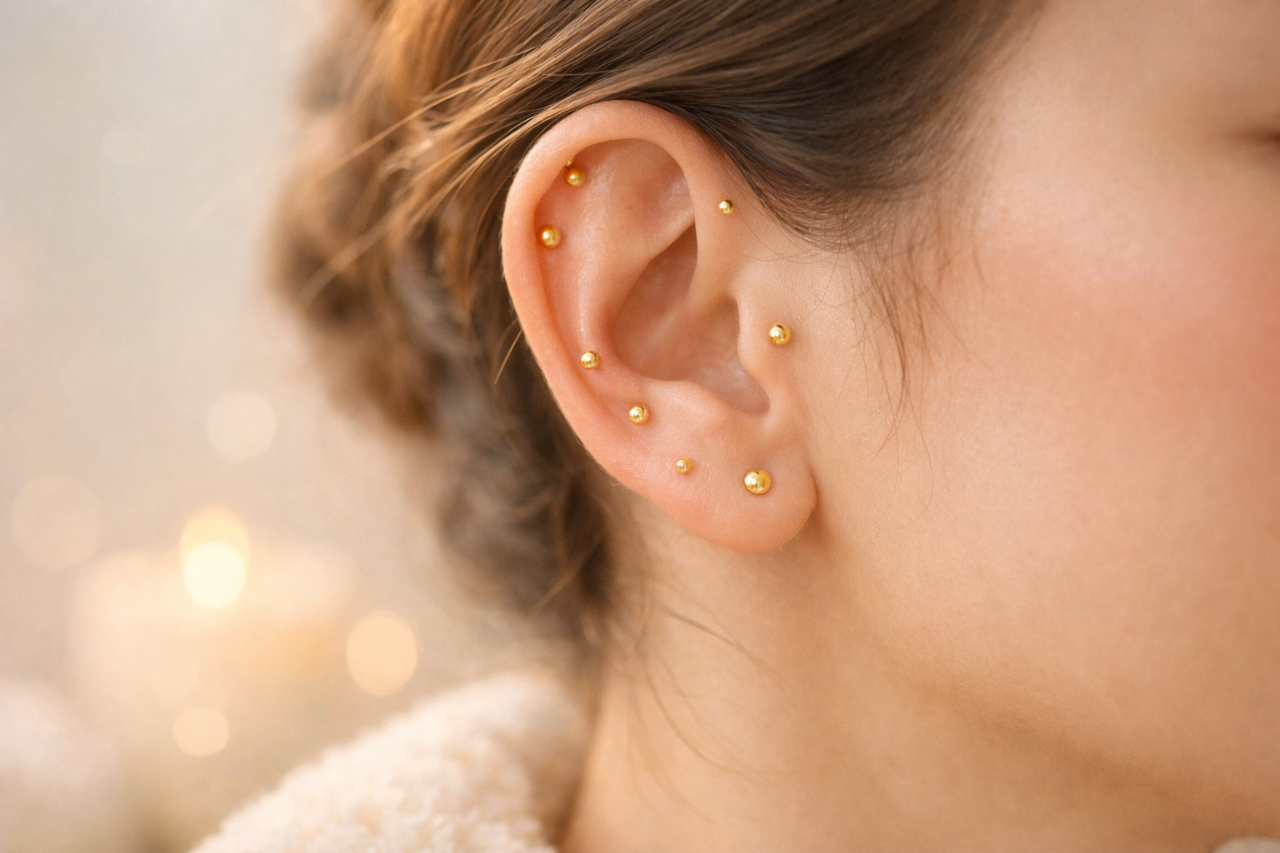
Why are my ear piercings bleeding?
Minor otorrhagia from piercing is common during the initial healing of a new piercing and it is not usually cause for concern. However, bleeding, along with symptoms like swelling, pain, and discharge, may signal a pierced ear infection. Identifying the cause, whether it's due to trauma, improper jewelry, or metal allergies, is crucial in preventing further complications.


Blood in baby's ear: cotton buds and ear infection
When parents or caregivers notice blood in the ear of a 1-year-old baby or see signs of ear bleeding in an 11-month-old baby, it can be quite distressing. This occurrence may be attributed to a couple of common causes, each warranting attention and, potentially, a visit to the pediatrician. Blood in a baby's ear can emerge from something as simple as a vigorous cleaning with a cotton bud or as a symptom of an underlying ear infection. Identifying the cause is crucial for ensuring the child receives appropriate care.
Causes of blood in a baby's ear:
Bleeding ear infections in children
Children's ear bleeding after cleaning with cotton
How to stop otorrhagia?
As hemorrhage from the ear is usually a symptom of another condition, recognizing the root cause is crucial. The bleeding will usually cease once the underlying cause is treated. Your healthcare professional may suggest various treatments, including:
- Antibiotics: If your otorrhagia stems from an infection, your healthcare provider may prescribe oral antibiotics or antibiotic ear drops. It is crucial to adhere diligently to the prescribed medication regimen for effective resolution.
- Ear tubes (Tympanostomy): In cases of recurrent ear infections, your healthcare provider might recommend ear tubes. This procedure involves the insertion of small, hollow tubes into your eardrum. These tubes facilitate the flow of air into the middle ear, allowing trapped fluids to drain.
- Object removal: Ear drainage can also result from foreign objects lodged in the ear canal. In such cases, prompt removal is essential. In most instances, healthcare providers can extract these objects during an office visit. However, severe cases may necessitate a referral to an otolaryngologist (ENT specialist).
- Surgical interventions and radiation therapy: In situations where ear cancer is suspected, your healthcare provider will refer you to an oncologist for further assessment and treatment. Common treatments for ear cancer typically involve surgical interventions and radiation therapy.
When should you consult a doctor?
You should consult a doctor if you or your child experience the following symptoms along with ear bleeding:
- Dizziness, drowsiness, and vomiting
- Severe ear pain
- Hearing loss
- Nosebleed or inability to follow movement with the eyes
- Ringing in the ears, head trauma, or altered state of consciousness
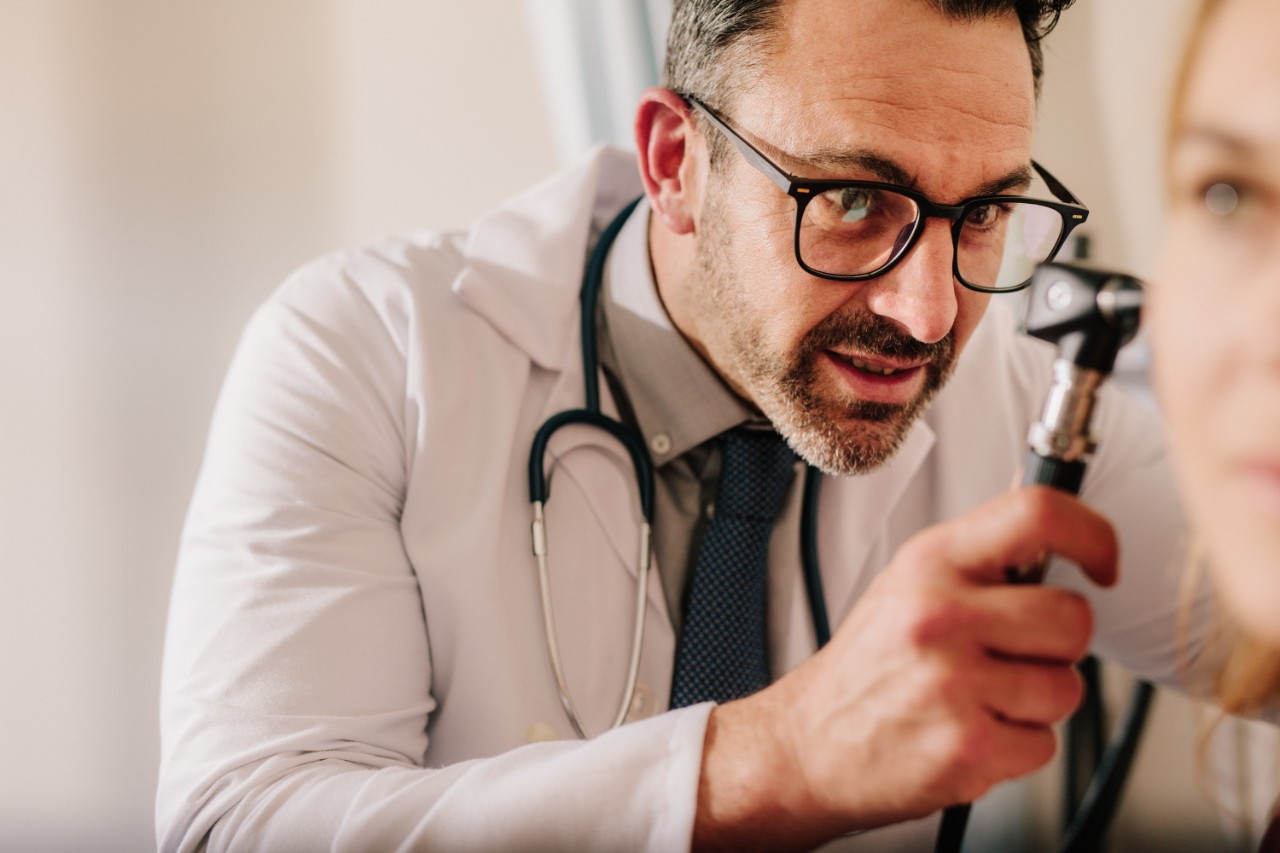
How the diagnosis process works
The initial examination of your ear bleeding will be conducted by your doctor, who will review your medical history and perform an otoscopy to diagnose if you're dealing with an eardrum inflammation or lesion. Depending on this diagnosis, you'll be prescribed either medication or referred to a specialist for further testing.
If the cause of your bleeding is left untreated, complications such as untreated otitis media causing damage to the skull and jaw bones, complete deafness from a head injury, permanent eardrum damage, and severe chronic inflammation of the ear canal, amongst others, may arise.
Never underestimate otorrhagia: complications
When left untreated, otorrhagia can give rise to a range of complications, the severity of which hinges on the diagnosis and associated symptoms:
- Neglecting otitis media may result in bone suppuration, leading to damage in the bones of the skull and jaw.
- Head injuries can escalate to complete deafness due to potential skull fractures and inner ear fluid leakage.
- In cases of head injuries with blood discharge from the ear, there's an increased risk of stroke.
- A damaged or perforated eardrum can suffer irreversible harm, affecting the proper vibration of the middle ear bones. Eardrum perforations can facilitate water entry, potentially causing more severe otitis media.
- Wounds in the ear canal area are susceptible to infection, which, in the worst-case scenario, can lead to otitis externa—a severe, chronic inflammation of the ear canal.
Addressing ear bleeding promptly is crucial in preventing these complications and preserving both your hearing and overall health.
Additional blood in ears FAQs
Earwax with blood: why is my earwax red?
If you notice that your earwax is red, it typically indicates the presence of blood, which can give the earwax a reddish tinge. This could be due to a number of reasons. Minor causes might include small abrasions in the ear canal, often resulting from scratching or the insertion of objects like cotton swabs, which can cause irritation or minor bleeding. More vigorous actions, such as aggressively cleaning your ears with cotton swabs, can also cause the delicate skin inside the ear canal to bleed, mixing with the earwax.
However, red or bloody earwax can also be a sign of more serious conditions. For example, a perforated eardrum, which may not only lead to red-streaked earwax but also to hearing loss and pain, can cause blood to appear in the earwax. Infections of the ear canal or middle ear can cause inflammation and sometimes bleeding. In rare cases, a growth or lesion in the ear canal might bleed, which then mixes with the earwax.
It's important not to ignore red or bloody earwax, especially if it's accompanied by other symptoms like ear pain, hearing loss, or discharge.
Why is my ear bleeding from inside?
How to stop inner ear bleeding?
Inner ear bleeding is a serious symptom that requires immediate medical attention. While waiting for professional care, there are several steps you can take to manage the situation and prevent further harm:
- Do not insert anything: Avoid putting cotton swabs, fingers, or any other objects into the ear.
- Positioning: Sit or lie down with the affected ear facing downward to allow gravity to assist with drainage.
- Apply a clean cloth: If there is external bleeding, gently place a clean cloth or sterile gauze against the outer ear.
- Avoid pressure: Do not press on the ear, as this may exacerbate the bleeding.
- Keep the ear dry: Refrain from getting the ear wet, which means no swimming or showering, to prevent infection.
- No ear drops: Avoid using over-the-counter ear drops or medications until evaluated by a healthcare provider.
- Seek medical care: Contact a healthcare professional or go to the nearest emergency room for an evaluation as soon as possible.
Remember, these steps are not a substitute for professional medical treatment but are meant to manage the situation temporarily until you can receive appropriate care.
Is ear pulsing linked to ear bleeding?
With you on your journey to better hearing.
It's time to finally treat your hearing loss. Sign up for a free consultation with a licensed hearing care professional today to determine if you have hearing loss. It’s the start of your journey towards better hearing.
EarPros benefits:
- It's 100% risk free
- Best partner with more than 1.000 stores






