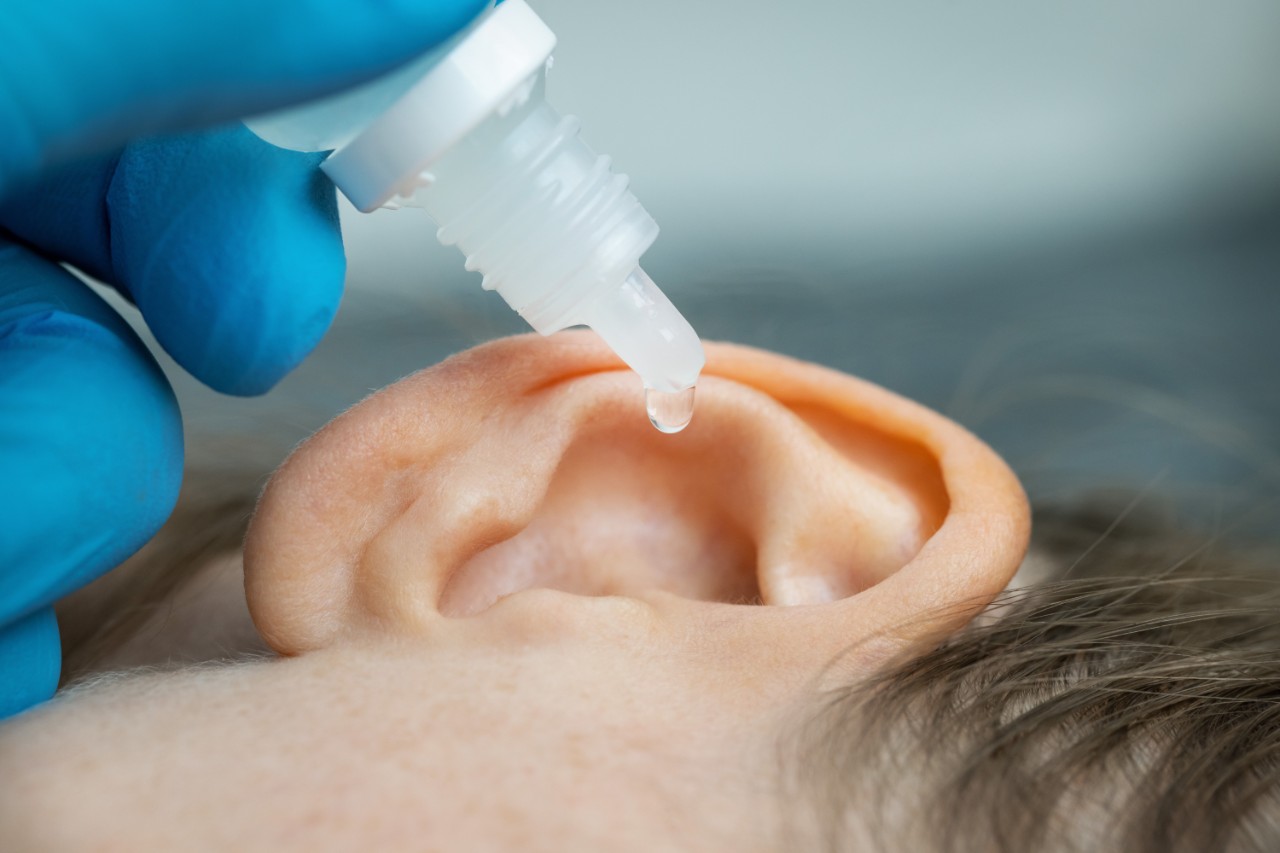
Types and effective ear drops usages for ear health

Ear drops are a specialized form of medication designed for direct application into the ear. These medications exist in a liquid state and are typically administered using a dropper or occasionally, a spray. The fundamental purpose of ear drops is to address a broad spectrum of ear-related ailments, including infections, inflammations, earwax buildup, and pain providing targeted treatment and swift relief.


Different types of ear drops
Antibiotic ear drops: usage and efficacy
Steroid ear drops: advantages and side effects
Antifungal ear drops: indications & purpose
Wax-softening ear drops: ear health management
Hydrating ear drops: maintaining ear moisture
Analgesic ear drops: pain management


The multifaceted uses of ear drops
Ear drops exhibit a wide array of applications, extending from the treatment of diverse ear infections to the management of earwax accumulation, alleviation of ear pain, addressing swimmer's ear, and other less prevalent uses.
1. Managing earwax build-up
An overproduction of earwax can lead to obstructions, hearing impairment, and discomfort. Wax-softening ear drops, also known as cerumenolytics, are utilized to soften and dissolve earwax, facilitating its removal. A study in the American Journal of Audiology discovered that cerumenolytic drops were effective in reducing earwax blockages, thereby circumventing the need for more invasive procedures.
2. Alleviating ear pain
Ear pain, or otalgia, can be triggered by various conditions, including ear infections, earwax blockages, and pressure fluctuations. Analgesic ear drops are employed to alleviate this pain. These drops often contain a local anesthetic, such as lidocaine, which numbs the ear and provides temporary relief. A systematic review in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management revealed that topical analgesics were effective in managing ear pain in children with acute otitis media.
3. Treating swimmer's ear
Swimmer's ear, or acute otitis externa, is an infection of the outer ear canal frequently caused by residual water in the ear post-swimming. This creates a moist environment that fosters bacterial growth. Preventive ear drops, usually acetic acid or alcohol-based, can aid in drying out the ear canal and creating an environment less hospitable to bacterial growth. Antibiotic ear drops are employed to treat swimmer's ear once an infection has set in. A study in the Archives of Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery found that acetic acid drops were effective in preventing swimmer's ear in children.
4. Other less common uses of ear drops
Apart from these common uses, ear drops also have some less recognized applications. For example, steroid ear drops can be employed to treat inflammatory conditions of the ear, such as eczema or dermatitis. Antifungal ear drops are utilized to treat fungal ear infections, which are less frequent but can pose management challenges. Hydrating ear drops can assist in managing dryness and itching in the ear canal, often caused by environmental factors or certain medications.


How to use ear drops?
Technique for adults
Administering ear drops correctly is paramount to ensure their effectiveness. For adults, the process is straightforward yet demands precision. Follow these detailed instructions:
- Begin by washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water to eliminate the risk of potential infection.
- Gently agitate the ear drop bottle, provided the instructions on the package advocate doing so.
- Either tilt your head sideways or recline with the afflicted ear facing upwards.
- To open up the ear canal, pull the outer ear gently backwards and upwards.
- Instill the prescribed number of drops into the ear with caution, ensuring the dropper does not touch the ear.
- Retain the same position for approximately five minutes to allow the medication to permeate deep into the ear canal.
- If deemed necessary, lightly insert a cotton ball into the ear to prevent leakage.
- If required, repeat the process for the other ear.
Administering ear drops to kids
Administering ear drops to children necessitates additional care due to their smaller and more sensitive ear canals. The steps largely mirror those for adults, with a few alterations:
- Position the child to lie down with the affected ear facing upwards.
- For children under three, draw the earlobe downwards and backwards; for older children, pull the earlobe upwards and backwards.
- Dispense the prescribed number of drops, ensuring the dropper does not come into contact with the ear.
- Encourage the child to remain still for a few minutes to allow the medication to take effect.
- If necessary, use a cotton ball to absorb any surplus drops.
Common mistakes in administering ear drops: how to avoid them
Despite the seemingly simple process, errors in administering ear drops are frequent. Here are a few common ones and how to circumvent them:
- Neglecting to shake the bottle: Some medications necessitate thorough mixing before use. Always adhere to the instructions on the package.
- Allowing the dropper to touch the ear: This can introduce bacteria and trigger infection. Maintain a safe distance between the dropper and the ear.
- Inadequate waiting time post administering the drops: It's crucial to allow the medication adequate time to reach its target. Endeavor to wait at least five minutes before altering positions.
- Employing ear drops with a perforated eardrum: This can result in pain and potential complications. Always seek advice from a healthcare professional before using ear drops if a perforated eardrum is suspected.
Tips and tricks for easy application
- Warm the bottle: Cold ear drops can induce dizziness. To bring it to body temperature, hold the bottle in your hand for a few minutes.
- Use a mirror: If visibility is an issue, use a mirror or seek assistance.
- Exercise patience: It takes time for the medication to take effect. Refrain from rushing the process.
- Follow up: If symptoms persist following a few days of treatment, seek consultation from a healthcare professional.

Ear drops side effects
Like all medications, ear drops may cause certain side effects. However, these are usually well-tolerated, with most individuals not experiencing any adverse reactions.
Common side effects may include:
- temporary discomfort or a stinging sensation in the ear
- a bitter taste if the medication drains into the throat
- potential allergic reactions to the ear drops' ingredients
In rare instances, prolonged use of specific ear drops may lead to ear canal infections or fungal infections. Adhering to the prescribed dosage and duration of use is crucial to minimize these risks.
Rare but serious side effects
Though infrequent, serious side effects can occur. These may include:
- severe allergic reactions, characterized by symptoms such as difficulty breathing, facial or throat swelling, and intense itching or rash
- persistent or worsening pain, changes in hearing, or dizziness
If you encounter any of these symptoms, seeking immediate medical attention is imperative. These symptoms could signify a more severe condition or a negative reaction to the medication.
Allergic reactions to ear drops
Allergic reactions to ear drops may arise due to sensitivity to one or more ingredients in the formulation. Symptoms can vary from mild itching or rash to severe reactions like anaphylaxis. If you notice any signs of an allergic reaction, such as hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat, discontinue use and seek immediate medical assistance. To prevent allergic reactions, it's vital to disclose any known allergies to your healthcare provider before using ear drops.
Ear drops for kids
Children, particularly those in their early years, are more prone to ear infections due to the structure of their Eustachian tubes and their still-developing immune systems. Ear drops, especially antibiotic ear drops, are pivotal in treating these infections. However, safety is a paramount concern when administering ear drops to children. The American Academy of Pediatrics advises that antibiotic ear drops should only be used when necessary and under a healthcare provider's guidance to avoid potential antibiotic resistance. Moreover, the correct technique of administration is vital to ensure the drops reach the middle ear without causing discomfort or injury.
Ear drops for adults
In adults, ear drops are commonly used for conditions such as earwax build-up and swimmer's ear. Wax-softening ear drops prove effective in managing excessive earwax, while antibiotic or steroid ear drops can treat swimmer's ear. For adults with chronic ear diseases, such as otitis media with effusion, long-term use of steroid ear drops may be recommended. However, adults must be aware of potential side effects, such as local irritation or allergic reactions. It's also crucial to consider interactions with other medications, especially in adults taking multiple drugs for various health conditions.
Ear drops for seniors
Seniors often face unique ear health challenges, including age-related hearing loss, increased earwax build-up, and a higher risk of infections due to decreased immunity. Hence, ear drops are an essential tool in managing their ear health. However, seniors may have more sensitive or dry skin in the ear canal, making them more susceptible to irritation from ear drops. Therefore, hydrating ear drops may be beneficial in this age group. Additionally, seniors may have difficulty administering ear drops due to physical limitations, necessitating assistance or alternative methods of application. It's also important to consider the potential for drug interactions, as many seniors take multiple medications for various health conditions.
Best ear drops on the market
When it comes to choosing the best ear drops available in the US, several products stand out for their effectiveness and quality. Here are some of the top options:
- Cortexi Ear Drops: Renowned for their all-natural ingredients that alleviate ear discomfort and promote overall ear health.
- Debrox Earwax Removal Aid: Effective in dissolving earwax safely and gently, making it a popular choice for ear care.
- Similasan Ear Relief Drops: Offers natural relief from ear pain and infections, ideal for those seeking a homeopathic solution.
- Murine Ear Drops: Provides quick relief from earwax build-up and discomfort, trusted by many for its fast-acting formula.
- Hyland's Earache Drops: Another excellent homeopathic option that helps relieve ear pain and irritation caused by minor infections.
Ear drops FAQs
What happens if you leave ear drops in too long?
If you leave ear drops in your ears for longer than recommended, the specific effects will depend on the type of ear drop and the active ingredients it contains. In general, leaving ear drops in too long might:
- Reduce their effectiveness: If ear drops are left in for much longer than the prescribed time, they might not work as effectively. This is because the medication may become too diluted or dispersed over time.
- Cause irritation or discomfort: Overexposure to certain medications can irritate the delicate skin of the ear canal.
- Increase the risk of side effects: Especially with antibiotic or steroidal ear drops, prolonged exposure could potentially increase the risk of side effects.
- Increase the risk of infection: If the ear remains moist for too long due to the ear drops, it could potentially create an environment conducive to bacterial or fungal growth, leading to infections like otitis externa (swimmer's ear).
- Wax accumulation: Some ear drops can cause earwax to soften and expand, and if not properly drained or cleaned, this could lead to a blockage.
- Temporary hearing reduction: This might be due to the physical presence of the liquid blocking sound waves. It usually resolves after the fluid has drained or evaporated.
It's important to always follow the instructions provided with the ear drops or as directed by a healthcare professional. If you believe you've left ear drops in for too long, or if you're experiencing discomfort, pain, or any other symptoms, it would be wise to consult with a healthcare professional or an ENT (ear, nose, and throat) specialist.
How long do ofloxacin ear drops take to work?
Why are ear drops important in ENT practice?
With you on your journey to better hearing.
It's time to finally treat your hearing loss. Sign up for a free consultation with a licensed hearing care professional today to determine if you have hearing loss. It’s the start of your journey towards better hearing.
EarPros benefits:
- It's 100% risk free
- Best partner with more than 1.000 stores