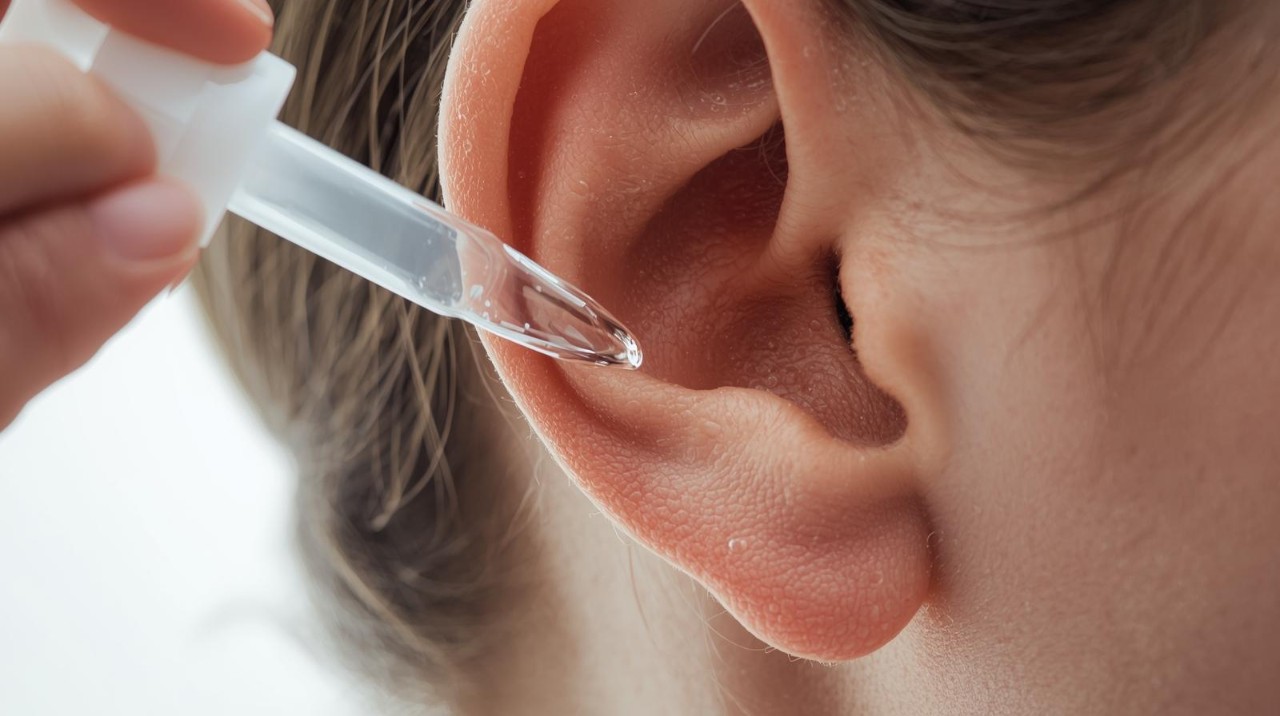
What is a fungal ear infection (otomycosis)?
A fungal ear infection, medically known as otomycosis, is an infection of the outer ear canal caused by fungi. Unlike typical bacterial ear infections, otomycosis often develops in warm, humid environments and is commonly caused by fungi such as Aspergillus and Candida species. Symptoms include itching, discomfort, discharge, and sometimes hearing difficulties. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and ensure effective healing.
What Clotrimazole is and what it is used for
Clotrimazole for swimmer's ear
What to know before using Clotrimazole
- Ensure the ear infection is fungal, as clotrimazole does not treat bacterial or viral infections.
- Consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis before starting treatment.
- Do not use clotrimazole if you have a perforated eardrum, unless directed by your doctor.
- Follow the prescribed dosage and duration carefully to avoid incomplete treatment and recurrence.
If symptoms worsen, or if you experience allergic reactions or irritation, stop using the medication and seek medical advice immediately-—this is particularly important during pregnancy to ensure safety for both mother and baby.

Forms of Clotrimazole
Clotrimazole comes in various forms to effectively treat different fungal infections, including:
- Creams – Used primarily for skin infections, providing a moisturizing antifungal effect.
- Lotions – Similar to creams but lighter, suitable for larger or hairy areas of skin.
- Powders – Help keep the affected area dry and prevent fungal growth, often used in moist areas.
- Topical solutions and ear drops – Specifically designed for direct application in the ear canal to treat fungal ear infections.
- Sprays – Convenient for easy application on the skin, especially for hard-to-reach areas or larger surfaces.
Possible side effects
While clotrimazole is generally well tolerated, some people may experience side effects, including
- Mild irritation or redness at the application site
- Itching or burning sensation
- Dryness or peeling of the skin around the treated area
- Allergic reactions such as rash, swelling, or severe itching (rare)
If any side effects worsen or continue, stop using the medication and contact a healthcare professional promptly.
How to use Clotrimazole antifungal ear drops
- Wash your hands thoroughly before applying the drops.
- Shake the bottle gently if the instructions say to do so.
- Tilt your head or lie down with the affected ear facing upward.
- Carefully place the prescribed number of drops into the ear canal.
- Avoid touching the dropper tip to your ear to prevent contamination.
- Keep your head tilted for a few minutes to allow the medication to penetrate.
- Use the drops exactly as prescribed, usually once or twice daily.
- Continue treatment for the full duration, even if symptoms improve.
- If you feel pain or irritation, stop use and contact your healthcare provider.
How long to leave clotrimazole in ear
After applying clotrimazole ear drops, it’s important to keep the medication inside the ear canal for several minutes to ensure effective treatment. Typically, you should keep your head tilted or lie on your side with the treated ear facing upward for at least 5 to 10 minutes.
This allows the drops to fully coat the ear canal and work against the fungal infection. Avoid wiping or rinsing the ear immediately after application to prevent removing the medication prematurely. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding duration and frequency of use for the best results.
How many drops of Clotrimazole in ear
Pediatric dose
In children, the use of clotrimazole ear drops should always be guided by a healthcare professional. The typical pediatric dose is usually 1 to 2 drops in the affected ear, twice daily, but this may vary depending on the child’s age, weight, and the severity of the infection.
It’s important for parents or caregivers to follow the prescribed instructions carefully and avoid self-medicating. If any signs of irritation, discomfort, or allergic reaction occur, stop the treatment and consult a doctor promptly.

How long to use Clotrimazole ear drops
Clotrimazole ear drops are typically used for 7 to 14 days, depending on the severity of the fungal infection and the response to treatment. Even if symptoms begin to improve within a few days, it is essential to continue using the drops for the full prescribed duration to ensure the infection is completely cleared. Stopping treatment too early can lead to a recurrence. Always follow your doctor’s instructions, and if symptoms persist beyond two weeks, consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation.
How to store Clotrimazole ear drops
Clotrimazole ear drops should be stored at room temperature, typically between 15°C and 25°C (59°F to 77°F), away from direct sunlight, heat, and moisture. Do not refrigerate or freeze the medication unless indicated on the packaging. Keep the bottle tightly closed when not in use, and always store it out of reach of children. Do not use the drops past their expiration date, and discard any unused medication according to local disposal guidelines or your pharmacist’s advice.


Price of Clotrimazole eardrops
In the United States, clotrimazole ear drops are generally available by prescription only, and their price can vary depending on the pharmacy and insurance coverage. Without insurance, the cost for a typical prescription bottle may range from $20 to $60.
While clotrimazole ear drops require a prescription, there are other over-the-counter ear drops available that treat minor ear infections or symptoms, but these usually do not contain clotrimazole. Generic versions of clotrimazole drops tend to be more affordable than branded products. To save on costs, it’s advisable to consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist about generic options and any available discounts.
Clotrimazole ear drops review
Clotrimazole ear drops are widely regarded as an effective treatment for fungal ear infections (otomycosis). Many users report relief from itching, discomfort, and discharge within a few days of starting treatment. The drops are generally well tolerated, with few experiencing mild side effects such as slight burning or irritation. Healthcare professionals often recommend clotrimazole for its targeted antifungal action and ease of use. However, some patients note that treatment requires consistent application over a full course, usually one to two weeks, to ensure complete clearance of the infection. Overall, clotrimazole ear drops receive positive reviews for their efficacy and safety when used as directed.
Alternative to clotrimazole ear drops
If clotrimazole ear drops are not suitable or effective, there are several alternative treatments available for fungal ear infections. Other antifungal medications such as miconazole, ketoconazole, or fluconazole may be prescribed by healthcare professionals. In some cases, combination ear drops containing antifungal and antibacterial agents, like chloramphenicol with clotrimazole or antibiotic-steroid blends, are used to address mixed infections or reduce inflammation. Additionally, proper ear cleaning and keeping the ear dry are important supportive measures. Always consult a healthcare provider before switching treatments to ensure the best and safest option for your specific condition.
Comparying eardrops for infections
Clotrimazole | Chloramphenicol | Beclomethasone | Lignocaine Hydrochloride | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Type |
Antifungal |
Antibiotic |
Corticosteroid |
Local anesthetic |
Primary use |
Treat fungal ear infections (otomycosis) |
Treat bacterial ear infections |
Reduce inflammation and swelling |
Relieve ear pain and discomfort |
Action |
Kills fungi by disrupting cell membranes |
Kills or inhibits bacteria |
Anti-inflammatory |
Blocks nerve signals |
FAQs about Clotrimazole eardrops
Are Clotrimazole ear drops painful?
Clotrimazole ear drops are generally not painful when applied correctly. Most users experience little to no discomfort during use. However, some people may feel a mild burning or stinging sensation shortly after application, which usually subsides quickly.
If you experience persistent pain, severe irritation, or worsening symptoms, it is important to stop using the drops and consult your healthcare provider. Proper application and following dosage instructions can help minimize any discomfort.
Is Clotrimazole safe for ears?
Clotrimazole is generally considered safe for treating fungal infections in the ear when used as directed. It specifically targets fungal cells without harming surrounding healthy tissue. However, it should only be used if the eardrum is intact, as using it with a perforated eardrum can cause irritation or complications.
It’s important to follow the prescribed dosage and avoid overuse. If you experience any adverse reactions like severe irritation, swelling, or allergic symptoms, stop using the medication and consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Can Clotrimazole and Neomycin be used together?
Clotrimazole and Neomycin are sometimes combined in ear drop formulations to treat infections that involve both fungal and bacterial components. Clotrimazole targets fungal infections, while Neomycin is an antibiotic effective against certain bacteria. Using them together can provide a broader spectrum of treatment, especially in mixed infections.
However, Neomycin can cause allergic reactions or ear irritation in some individuals, so it’s important to use such combination products only under medical supervision. Always follow your healthcare provider’s advice regarding the use of multiple medications in the ear.
Can Clotrimazole in ears cause a fever?
Clotrimazole ear drops themselves do not typically cause fever as a side effect. Fever is usually a sign of an underlying infection or the body’s response to inflammation. If you develop a fever while using Clotrimazole in your ears, it may indicate that the infection is worsening or spreading, or that a bacterial infection is present alongside the fungal one.
In such cases, it’s important to seek medical advice promptly to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment. If you experience fever along with increased pain, swelling, or discharge, stop using the drops and contact your healthcare provider immediately.
What happens if I use an overdose of eardrops?
Using more eardrops than recommended can increase the chance of side effects such as irritation, redness, or a burning sensation in the ear. Overdosing on ear drops usually does not cause serious harm, but it can worsen discomfort or cause temporary swelling. It does not speed up healing and may interfere with the treatment process.
If you accidentally use too many drops, avoid further application until you can consult a healthcare professional. In case of severe pain, swelling, or signs of an allergic reaction, seek medical attention promptly.
Can you use Clotrimazole with perforated eardrum?
Clotrimazole ear drops are generally not recommended for use if you have a perforated (ruptured) eardrum unless specifically advised by a healthcare professional. A perforated eardrum creates an opening between the ear canal and the middle ear, which may allow the medication to enter areas where it could cause irritation or damage.
Using ear drops with a perforated eardrum can increase the risk of complications such as ear pain, infection, or hearing problems. If you suspect your eardrum is perforated, it’s important to consult a doctor before using any ear drops.
** Some images in this article were generated using artificial intelligence.
With you on your journey to better hearing.
It's time to finally treat your hearing loss. Sign up for a free consultation with a licensed hearing care professional today to determine if you have hearing loss. It’s the start of your journey towards better hearing.
EarPros benefits:
- it's 100% risk free.
- best partner with more than 1.000 stores