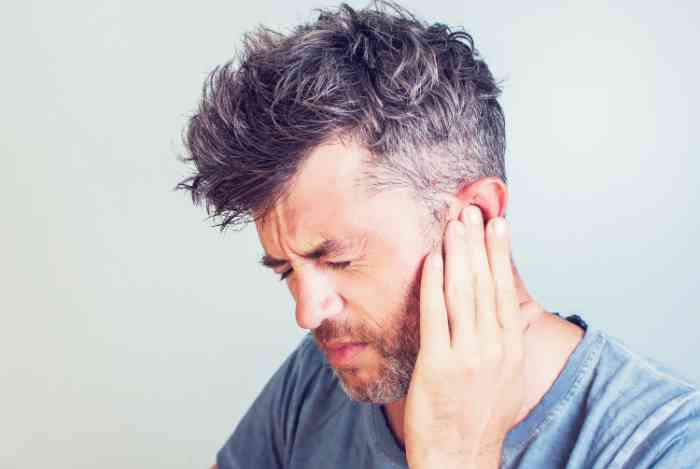
Cervical tinnitus: neck pain and ringing in ears

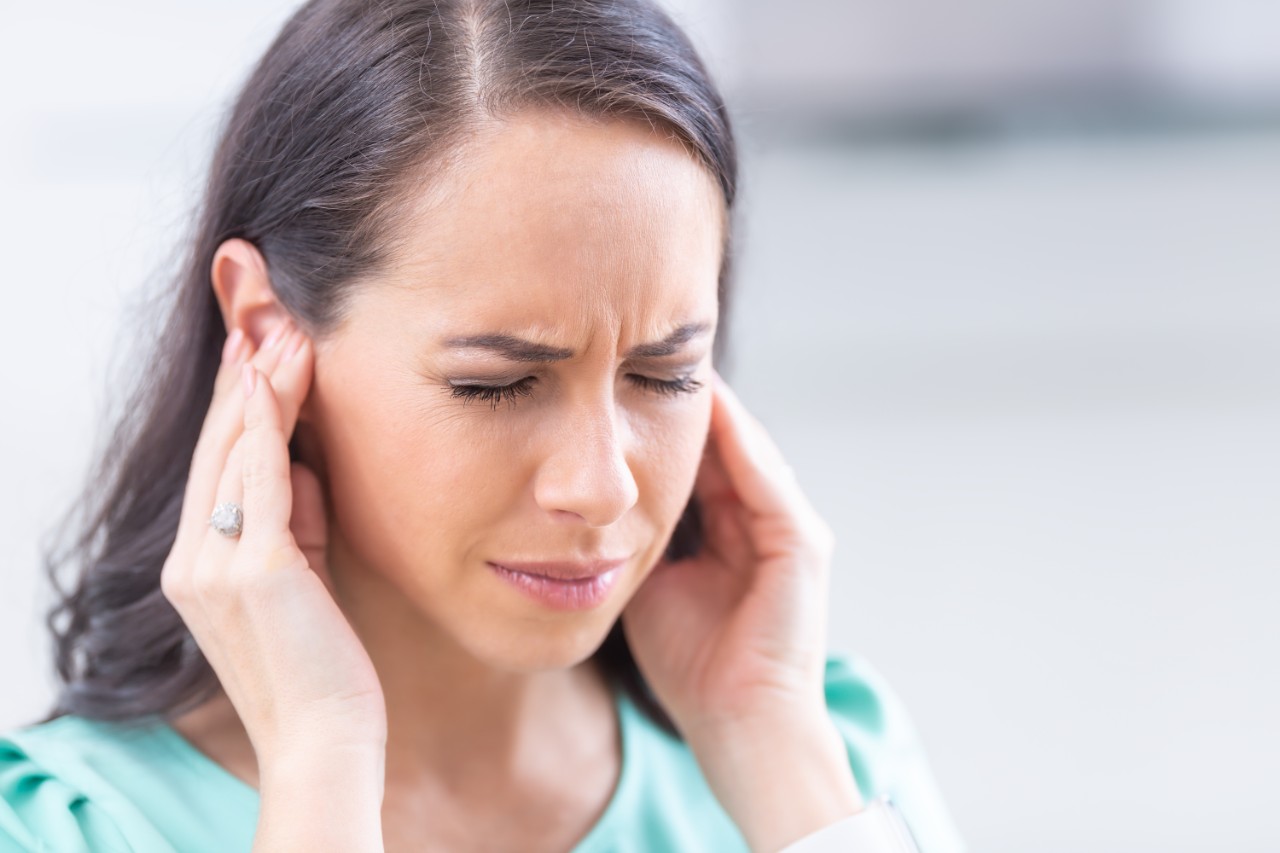
Hearing sounds such as buzzing or ringing in the ears can be a sign associated with various conditions including the so-called cervical tinnitus.
What is cervical tinnitus?
Cervical tinnitus is a distinctive auditory condition characterized by a persistent ringing sensation in the ears, specifically originating from the cervical region, which pertains to the back of the neck often leading to the manifestation of painful neck and ear. This auditory anomaly is closely linked to issues within the cervical spine or muscle tension in the neck area.
Symptoms of cervical tinnitus
Cervical tinnitus manifests itself through an array of distinct symptoms, offering vital indicators for individuals to recognize this condition.
Common signs include:
- Persistent ringing sound in the ears, originating specifically from the cervical region
- Heightened sensitivity to certain noises, along with muscle tension and discomfort in the neck area
- Perceive changes in hearing acuity
- Dizziness or a sense of imbalance
As these symptoms can significantly impact one's quality of life, seeking professional medical guidance is imperative for a thorough evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and tailored management plan. Early identification of cervical tinnitus symptoms enhances the prospects of effective intervention and improved outcomes.
Tight neck muscles causing ear problems
Cervical tinnitus causes are various and associated with the vulnerability of the neck, a commonly afflicted area prone to pain. When tinnitus is present, individuals frequently encounter neck tension, originating from the cervical spine, which can impact the function of cranial nerves and result in ear ringing.
Several causes contribute to cervical tinnitus, including:
- Exposure to cold snaps leading to a stiff neck
- Incorrect posture
- Prior traumas
- Whiplash injuries
- Stress and anxiety
- Arthritis in the cervical vertebrae
- Lifting heavy loads during physical activity
- Sleeping in an improper neck position
Trauma to the spine, such as falling on the back, may alter labyrinth fluid pressure, causing cervical tinnitus. Additionally, muscle tension in the middle ear can transmit misleading signals along the nerve pathway, prompting the brain to react with tinnitus and dizziness. Consulting with a specialist is essential to comprehend the specific type of tinnitus experienced and to guide individuals toward the appropriate course of action for effective management.


Exercises for cervical tinnitus relief
Cervical tinnitus can be effectively treated by addressing the underlying issues and concurrently mitigating neck pain and ringing in the ears.
In cases where cervical tinnitus is linked to posture or physical factors, collaboration with a medical professional or physiotherapist becomes instrumental in resolving the associated discomfort.
Complementary treatments, such as targeted massages focusing on localized pain, prove beneficial, particularly in alleviating muscle spasms. Engaging in specific neck exercises tailored for tinnitus can also be recommended as part of a comprehensive approach to managing symptoms.
For persistent pain, exploring drug therapies under the guidance of a doctor may be considered, providing additional avenues for comprehensive and personalized treatment to enhance the overall well-being of individuals dealing with cervical tinnitus.
1. Neck exercises and massages for tinnitus
Among cervical tinnitus exercises, rehabilitative neck exercise stands out as a well-established and proven remedy for addressing this condition. When conducted under the guidance of an osteopath, physiotherapist, or a qualified professional in the field, these exercises can contribute significantly to pain reduction. The sessions with these specialists involve targeted movements designed to relax contracted muscles, offering tangible relief for individuals grappling with cervical tinnitus.
Additionally, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) emerges as another potential solution, employing low-voltage electrical currents to alleviate pain associated with cervical tinnitus. In this therapy, small adhesive pads are affixed to the skin, producing a tingling sensation that aids in muscle relaxation and pain alleviation.
2. Physiotherapy to tackle cervical tinnitus


The strategic application of physiotherapy and trigger point massages helps address the root causes of cervical tinnitus, promoting relaxation and improved well-being.
However, it is crucial to exercise caution and seek expert advice before attempting any exercises independently, as inappropriate techniques may exacerbate symptoms rather than alleviate them.
3. Sound enrichment therapy and tinnitus masker
Remedies for cervical tinnitus, particularly when linked to neck tension or objective tinnitus, often result in relief once the underlying causes are identified and treated. During the transitional phase, sound enrichment aids prove valuable in managing symptoms. Sound enrichment therapy works by reducing the volume of tinnitus through consistent stimulation of hearing, emitting nature-based sounds like streams, waterfalls, or rainfall. This continuous auditory experience can effectively alleviate the intensity of tinnitus, and in some instances, even lead to complete disappearance of the ringing in the ears.
Another viable treatment option is the use of a tinnitus masker, an electronic hearing aid device that produces and emits either broad-band or narrow-band noise at low levels, providing additional avenues for effective symptom management.


Can tight neck muscles cause pulsatile tinnitus?
Tight neck muscles can indeed contribute to the onset of pulsatile tinnitus, adding to the array of neck-related issues associated with ringing in the ears. The experience of pulsatile tinnitus often stems from compromised circulation to the blood vessels and arteries in the head, especially those in proximity to the ear.
- Factors such as poor blood flow to cranial nerves can be implicated in the manifestation of this condition.
- Additionally, trauma to the head and neck may increase the likelihood of experiencing pulsatile tinnitus, further affirming the interconnection between these two conditions.
- Noise pollution, including prolonged use of earphones and certain medications like antibiotics, is also recognized as a potential contributor to rhythmic pulsations.
FAQs about cervical tinnitus
Can cervical spondylosis cause tinnitus?
Can cervical tinnitus be cured?
What does cervical tinnitus sound like?
With you on your journey to better hearing.
It's time to finally treat your hearing loss. Sign up for a free consultation with a licensed hearing care professional today to determine if you have hearing loss. It’s the start of your journey towards better hearing.
EarPros benefits:
- it's 100% risk free.
- best partner with more than 1.000 stores