Key takeaways
- Bleeding from the ear (otorrhagia) can result from infections, trauma, foreign objects, or eardrum damage, with causes ranging from minor irritation to serious medical conditions.
- Common triggers include otitis, improper cotton bud use, ear piercings, barotrauma, and head injuries, producing symptoms such as pain, discharge, hearing changes, or dizziness.
- Treatment depends on the cause and may involve antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medication, careful cleaning, watchful waiting, or surgery in severe cases.
Experiencing blood in the ear, also known as otorrhagia, can be a cause for concern, prompting the need to delve into its various causes and how to address each scenario. This article aims to explore the diverse reasons behind ear bleeding, ensuring a comprehensive understanding for those seeking information.
Blood from ear: causes
Ear bleeding inside the ear can stem from various factors, with some being more severe than others. Otorrhagia typically arises from common causes such as:
1. Otitis
The occurrence of blood in the ear due to otitis is a common concern for individuals grappling with this painful ear infection. Otitis, whether in its middle form (otitis media) or external form (otitis externa), can result in ear bleeding as one of its symptoms.
In otitis media, an infection in the middle ear can lead to the accumulation of pus and fluid behind the eardrum. As this buildup exerts pressure on the eardrum, it can cause intense pain and, in certain instances, bleeding from the ear. Significantly, bleeding often signals that the infection has advanced, necessitating prompt medical attention.
In the case of otitis externa, also referred to as "swimmer's ear," the infection impacts the ear canal and the overlying skin. This infection can trigger itching, redness, swelling, and, at times, bleeding from the ear due to irritation and scratching. Otitis externa is frequently accompanied by pain and may demand medical intervention to alleviate symptoms and avert potential complications.
For both types of otitis externa, appropriate treatment involves the prescription of antibiotics to combat the infection, along with analgesics to alleviate pain. Moreover, it is imperative for a healthcare professional to examine the ear, assessing the infection's severity and determining the suitable course of treatment.
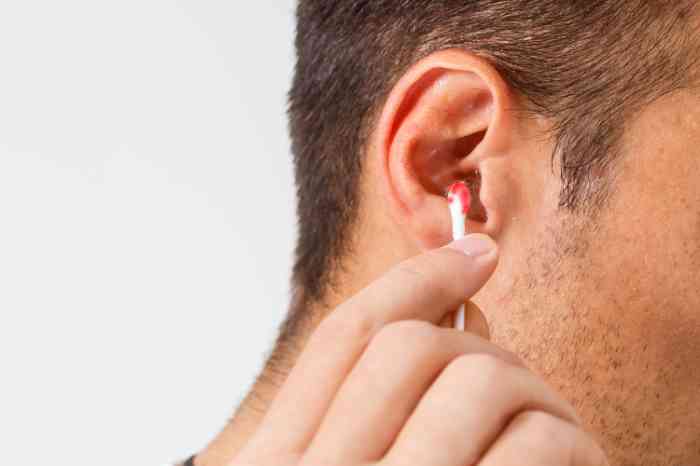
2. Ear cleaning using cotton buds
Ear bleeding after cleaning with a Q-tip or cotton bud may indicate improper practices, such as using them incorrectly, leading to potential ear issues and the need for cautious cleaning methods. This is often caused by the presence of a small sore or superficial wound inside the ear canal, a result of the frequent and incorrect use of these tools, which is a common practice in many ear cleaning routines.
The continuous rubbing of the cotton bud against the delicate walls of the ear canal can result in surface tearing or, in severe cases, lead to the rupture or perforation of the eardrum. In less severe instances, individuals may not experience pain but might observe blood on the cotton swab or a combination of blood with earwax. More serious cases may involve ear pain and hearing difficulties, often accompanied by temporary hearing loss.


Think you know everything about hearing health?


How much do you really know?
Take the quiz and find out!
👂 Test yourself! Every level unlocks new insights into hearing aids and hearing health.
🔎 Learn, explore, and challenge yourself with fun questions.
🎯 Start playing now and discover all the answers!
Less frequent cases for ear bleeding
Fungal ear infection (otomycosis)
Wounds
Head injuries
Skin irritation
Barotrauma: air or water in ear
High blood pressure
Cancer
A perforated eardrum


Types of blood in the ear
- Bloody pus in the ear: Associated with ear infections, this type indicates an ongoing infection requiring medical treatment.
- Blood plug in the ear: Blood clots in the ear canal, caused by injury or irritation, can partially or completely block the ear.
- Bloody earwax in the ear: Blood in ear wax indicates injury to the ear canal or a perforated eardrum, necessitating medical evaluation.
- Bloody fluid in the ear: It may indicate internal injury or a progressed infection, requiring professional evaluation.
- Dried blood in ear: It may suggest a past injury, recent trauma, or a healed ear canal wound. While the dried blood itself might not be an urgent concern, it's essential to investigate the underlying cause.
Earrings and piercing bleeding
The skin surrounding a new piercing may exhibit temporary swelling, redness, and tenderness, accompanied by slight bleeding. To minimize the risk of bleeding and infection, it's vital to choose a skilled and experienced piercer, maintain a sterile environment, and adhere to recommended aftercare practices. If an infected ear piercing keeps bleeding persists or signs of prolonged infection, such as persistent swelling, enduring redness, or excessive bleeding beyond the initial days, arise, seeking advice from a medical professional is crucial. Timely intervention can help prevent potential complications, emphasizing the importance of good hygiene and following care instructions for an optimal ear piercing experience.
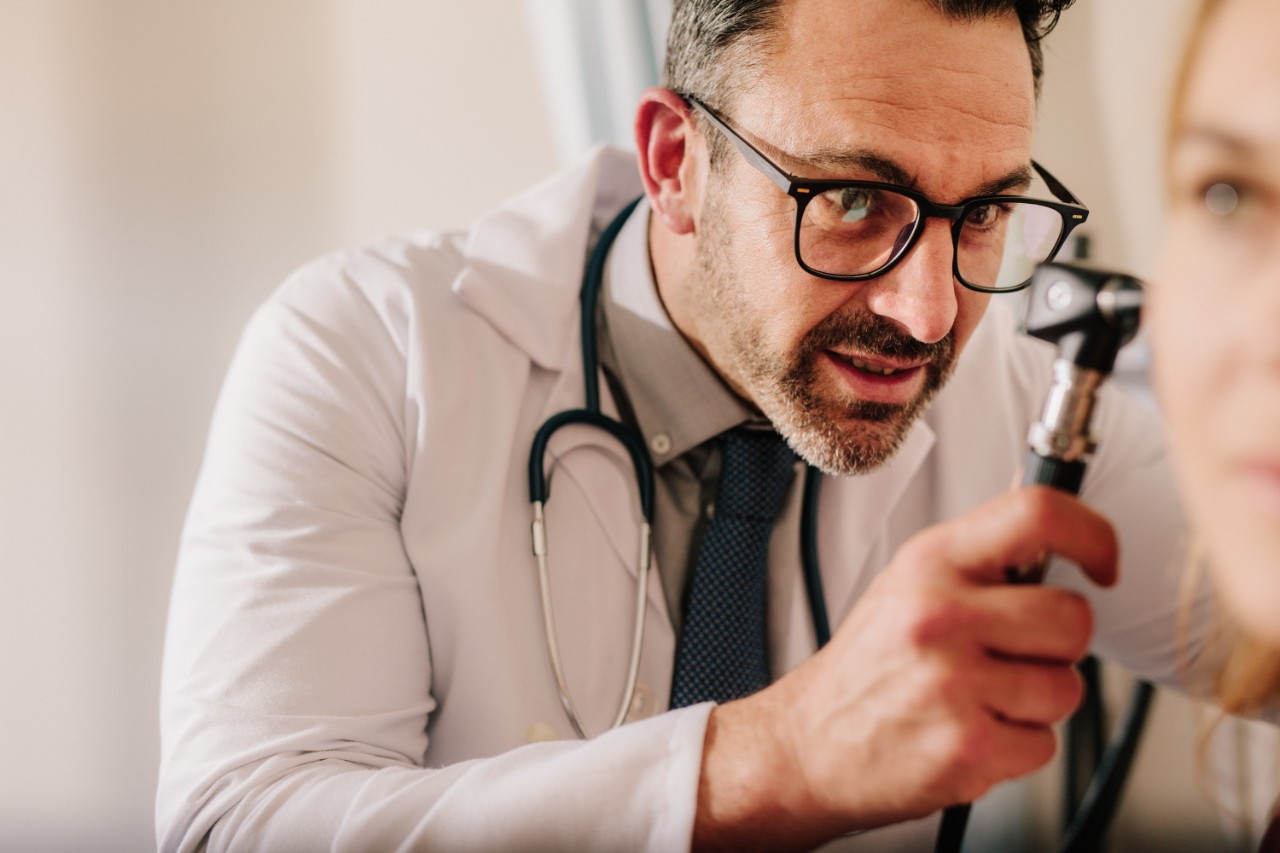
Diagnosis
Your initial point of contact for ear bleeding concerns is your doctor. Following a thorough examination of your medical history, they will conduct an otoscopy—a procedure involving the insertion of a tool into the ear to assess potential inflammation or eardrum lesions.
Based on the diagnosis, the doctor may recommend medication or refer you to a specialist for more extensive testing. It's important to mention that if the bleeding results from head trauma, a CT scan or MRI may be prescribed to detect any skull fractures.
With you on your journey to better hearing.
It's time to finally treat your hearing loss. Sign up for a free consultation with a licensed hearing care professional today to determine if you have hearing loss. It’s the start of your journey towards better hearing.
EarPros benefits:
- it's 100% risk free.
- best partner with more than 1.000 stores
Thank you for submitting your request
We will get in touch with you as soon as possible.Blood in ear in adults
In adults, bleeding in the ear can stem from various causes, ranging from minor injuries to serious conditions like infections or cancer, emphasizing the need for consultation with a doctor.
Blood in ear in children


In children and infants, blood in the ear may be a concern for parents, with common causes including otitis, ear pain, unintentional manipulation, or injury.
When a child's ear exhibits signs of bleeding, it may be attributed to otitis media, commonly known as a middle ear infection. Additional indicators of otitis media involve pronounced fatigue and elevated body temperature. In the case of a middle ear infection, the middle ear tends to accumulate fluid or pus. Fortunately, middle ear infections often resolve spontaneously over time.
Seeking medical attention is crucial for a proper diagnosis.
Bleeding ear during pregnancy


Bleeding from the ear during pregnancy is an unusual and concerning occurrence that requires prompt medical attention.
Ear bleeding could be a result of various factors, such as infections, trauma, or changes in blood flow. Infections might lead to inflammation and subsequent bleeding, emphasizing the importance of maintaining good ear hygiene. Trauma or injury to the ear, possibly due to accidental impacts or improper cleaning, could also contribute to bleeding. Additionally, hormonal changes during pregnancy might affect blood vessels, making them more susceptible to bleeding. Any instance of ear bleeding should be thoroughly examined by a healthcare professional to determine the precise cause and ensure the well-being of both the expectant mother and the baby.
Hearing blood pumping in one ear: Tinnitus


If you hear blood pumping in one ear, it is unrelated to ear bleeding; it is likely caused by pulsatile tinnitus.
Pulsatile tinnitus, characterized by rhythmic pulsations in the ear, may be associated with circulatory issues, and it's noteworthy that fluctuations in blood pressure can contribute to this condition. Specifically, individuals with high blood pressure may experience pulsatile tinnitus as a manifestation of the increased vascular activity. Alongside circulatory factors, various lifestyle elements can also play a role, such as prolonged exposure to noise pollution from activities like using earphones, the extended use of certain medications like antibiotics and diuretics, or experiencing any trauma to the head and neck. A medical professional can conduct a thorough examination of the head and neck to diagnose pulsatile tinnitus and determine the appropriate course of action for managing both the symptoms and any underlying blood pressure concerns.
What occurs if there is blood discharge from the ear?
The experience of ear bleeding can manifest with varying levels of pain. The intensity of pain or discomfort hinges on the root cause. It is imperative not to downplay ear bleeding and to promptly seek medical attention for precise diagnosis and suitable treatment.


Presence of blood in baby's ear wax
Bloody earwax in babies or children is typically the result of minor injuries, accompanied by minimal ear bleeding and small amounts of blood present in the earwax. These cases often resolve spontaneously.
If additional symptoms are present, it is advisable to contact your doctor to prevent potential long-term complications such as hearing loss or meningitis that may arise from an infection.
Indeed, another possible cause of ear bleeding in infants and children could be otitis media. Signs include severe exhaustion and fever in children.
Ear bleeding with or without pain
Ear bleeding can manifest as painless or with pain. Regardless of the presence of pain, monitoring ear bleeding is imperative as it can indicate an underlying issue. At times, ear bleeding may present as blood in the earwax rather than a direct flow of blood from the ear.
Various factors can contribute to ear bleeding, ranging from minor sores induced by the improper use of a cotton swab or Q-Tip to more serious causes such as head injuries or acoustic trauma. In instances where more severe causes are at play, the eardrum may be injured or perforated, often accompanied by intense pain concurrent with ear bleeding.
How to stop a bleeding ear: treatments
- Ointments or antihistamines: Prescribed to alleviate skin irritations or allergies in the ear canal.
- Superficial cleaning: Essential in cases of minor wounds or scrapes to prevent infection.
- Antibiotics: Administered to combat infection in the case of ear infections.
- Watchful Waiting: When ear bleeding results from superficial wounds in the ear canal or minor eardrum injuries, a period of watchful waiting is often sufficient, as the bleeding tends to naturally subside after a short duration.
- Anti-inflammatory medication: In cases where an ear infection is the instigating factor for ear bleeding, healthcare providers may prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs to counter inflammation. Additionally, antibiotic or antiviral drugs might be administered to address the infection.
- Surgery: In instances of particularly severe conditions, surgical intervention may be necessary. This is especially relevant in cases of severe tympanic perforation or extensive head trauma.
- Pain-relieving medication: Depending on the circumstances, healthcare professionals might opt to prescribe pain-relieving drugs, sedatives, antiemetic drugs, and more to manage associated symptoms accompanying ear bleeding.


When to seek medical advice


Here's a guide on when to seek the expertise of a medical professional:
- Experiencing dizziness, drowsiness, and vomiting
- Severe pain in the ear region
- Nosebleed
- Difficulty following eye movements
- Tinnitus
- Head trauma
- Altered state of consciousness
Potential risks and complications of ear bleeding
Failure to address the underlying cause of ear bleeding may result in various complications, contingent upon the diagnosis and observed symptoms:
- Neglected otitis media has the potential to induce bone suppuration, causing harm to the bones within the skull and jaw.
- In the case of a head injury, the risk of complete deafness may arise, stemming from possible complications such as a skull fracture and potential leakage of inner ear fluid. Ear bleeding following a head injury could also signify an elevated risk of stroke.
- A damaged or perforated eardrum may experience irreversible harm, affecting the proper vibration of the bones in the middle ear. An eardrum perforation creates a pathway for water entry, increasing the susceptibility to more severe otitis media.
- Injuries to the ear canal region, when untreated, may become infected, potentially leading to otitis externa—a severe and chronic inflammation of the ear canal.
Regardless of the specific treatment, it is vital to seek the expertise of an ear, nose, and throat specialist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention. Symptoms associated with ear bleeding should not be underestimated, as they may signify underlying medical conditions necessitating immediate attention.