Cochlear implants vs hearing aids: Both hearing aids and cochlear implants serve to amplify sounds, aiding individuals in their auditory perception. Unlike hearing aids, cochlear implants require surgical intervention. This article delves into the difference between cochlear implants and hearing aids and the factors to ponder before purchasing these devices.
Hearing aids
Hearing aids are compact electronic devices worn either in or behind the ear, designed to amplify sounds and improve auditory perception for individuals with mild to moderate hearing impairment. Available in diverse styles, they typically comprise three integral components collaborating to facilitate hearing:
- A microphone captures incoming sounds, transforming them into digital signals
- An amplifier boosts the intensity of the digital signals
- A speaker delivers the amplified sound into the ear canal
Pros
- Enhance phone conversations: Many modern hearing aids offer Bluetooth connectivity, allowing seamless streaming of phone calls directly to your devices
- Improved comfort in various listening environments: Initially, you may find certain sounds intrusive, but as your brain acclimates, you'll become better at filtering them out
- Reduced background noise interference: Hearing aids equipped with directional microphones prioritize speech, making it simpler to ignore surrounding noise
- Enhance communication: Engaging in social interactions reduces the risk of social isolation, depression, and cognitive decline linked to untreated hearing loss
Cons
- Hearing aid feedback: It occurs when sound intended for your ear canal instead escapes and re-enters the hearing aid microphone, resulting in a bothersome whistling noise
- Wax buildup: In-the-ear hearing aids can become obstructed by earwax, impeding sound transmission into your ear
- Regular upkeep: Hearing aids necessitate routine maintenance and may require replacement every few years
- Limitations: For individuals with severe to profound hearing loss, hearing aids may not provide sufficient assistance, leading to the consideration of cochlear implants as an alternative solution
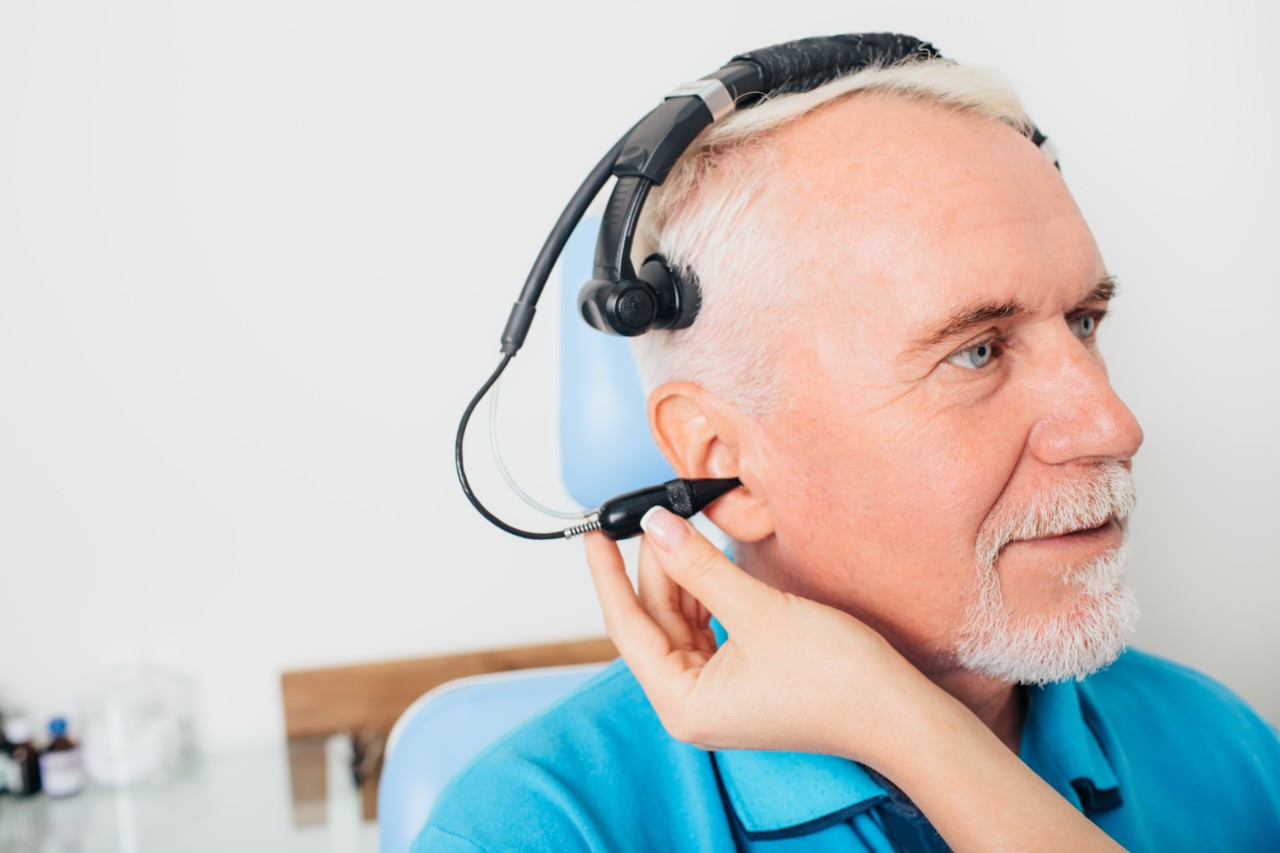


Cochlear implant
Cochlear implants have revolutionized the lives of individuals with severe hearing impairment, providing an opportunity to partially restore hearing capability. Similar to hearing aids, they do not fully restore natural hearing. However, unlike hearing aids, cochlear implants capture sound and transmit it directly to the auditory nerve through the cochlea. Cochlear implants are electronic devices implanted surgically into the inner ear, operate by circumventing impaired portions of the ear and directly activating the auditory nerve.
Primarily recommended for individuals with severe to profound hearing loss unaided by conventional hearing aids, cochlear implants offer an alternative solution.
There are three primary types of cochlear implants:
- Single-channel implants utilize a solitary electrode for stimulating the auditory nerve
- Multi-channel implants employ multiple electrodes, ensuring more accurate stimulation
- Hybrid implants blend the advantages of both single-channel and multi-channel designs, employing both types of electrodes to optimize hearing capability
Pros
- Cochlear implants have the potential to significantly enhance an individual's quality of life by improving their ability to perceive sound
- Research indicates that cochlear implants can lead to improvements in speech perception, communication skills, and overall social functioning
- They can also enhance the enjoyment of music and other auditory experiences for individuals with hearing loss
Cons
- Cochlear implants necessitate surgical intervention, which inherently carries risks
- Not everyone may benefit from cochlear implants, and there is an adjustment period required to acclimate to the new sounds and sensations provided by the implant
- Cost is a significant consideration, as cochlear implants can be expensive and may not be covered by insurance
Are cochlear implants better than hearing aids?


Price
In Australia, the prices of hearing aids and cochlear implants can vary depending on several factors, including the type and brand of the device, the level of technology, and any additional features or accessories included. Here's a general idea of the price range for each:
- Basic hearing aids: $500 to $2,000 per pair
- Mid-range hearing aids: $2,000 to $5,000 per pair
- Premium hearing aids: $5,000 to $10,000+ per pair
- Cochlear implant surgery (including device): $30,000 to $50,000+
- Additional costs may include pre-surgery assessments, post-surgery rehabilitation, and ongoing maintenance and accessories.
Insurance coverage
In Australia, the availability and extent of insurance coverage for hearing aids and cochlear implants can vary depending on factors such as the type of insurance plan, the individual's eligibility criteria, and the specific policies of insurance providers. Here's a general overview:
- Hearing Aids: In Australia, the government's Hearing Services Program provides eligible individuals with access to free or subsidized hearing aids and related services through accredited providers. Additionally, private health insurance plans may offer coverage for hearing aids, although the extent of coverage can vary between policies. It's essential to check with your private health insurer to understand the level of coverage available for hearing aids under your plan.
- Cochlear Implants: Cochlear implantation surgery and related costs are typically covered by Australia's public healthcare system (Medicare) for eligible individuals, including children and adults who meet specific criteria for severe to profound hearing loss. Private health insurance plans may also offer coverage for cochlear implants, although coverage details and out-of-pocket expenses can vary between policies. It's advisable to check with your private health insurer to understand the level of coverage available for cochlear implants under your plan.
Effectiveness
In terms of efficacy, both hearing aids and cochlear implants are highly effective in enhancing hearing abilities. Nevertheless, cochlear implants are typically deemed more effective for individuals with severe to profound hearing loss, whereas hearing aids are often preferred for those with mild to moderate hearing loss. Research indicates that cochlear implants can notably enhance speech recognition and sound localization in individuals with severe to profound hearing loss, whereas hearing aids may not deliver sufficient amplification for those with more severe hearing impairment.
Maintenance
It's worth noting that cochlear implants offer a maintenance advantage compared to hearing aids.
While hearing aids necessitate routine cleaning and battery changes, cochlear implants typically only require occasional maintenance appointments with a healthcare provider. However, it's crucial to emphasize that consistent usage is essential for both hearing aids and cochlear implants to preserve their effectiveness. Individuals who do not use their devices regularly may experience a deterioration in their hearing abilities over time.
Other factors to consider
Age
Lifestyle
Personal preference
Communication needs


Bimodal cochlear implant hearing aid
The bimodal solution, which involves a cochlear implant combined with a hearing aid, may be ideal for some people. This type of solution often helps to understand speech in noisy conditions and provides a better understanding of where the sound is coming from.
FAQs about cochlear implants & hearing aids
Cochlear implants/hearing aids: what's the sound?
What do cochlear implants & hearing aids sound like?
Cochlear implants and hearing aids produce different auditory experiences due to their distinct mechanisms of action:
- Hearing Aids: Hearing aids amplify sounds and deliver them to the ear canal. The sound experienced with hearing aids typically resembles natural sound but may be slightly amplified or modified depending on the individual's hearing loss and the settings programmed into the device. With modern digital hearing aids, sound quality is often clear and natural, with advanced features such as noise reduction and feedback cancellation enhancing the listening experience.
- Cochlear Implants: Cochlear implants bypass the damaged parts of the inner ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve, providing a sensation of sound to the brain. The sound perceived with cochlear implants may differ from natural hearing and can vary among individuals. Initially, recipients may perceive sounds as different or synthetic compared to natural hearing. With time and auditory rehabilitation, many recipients adapt to the new auditory sensations and report improvements in speech understanding and sound perception.
In summary, hearing aids aim to amplify natural sounds, while cochlear implants provide a sensation of sound through electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve. Both devices play vital roles in addressing hearing loss and improving communication abilities, albeit through different means.
How are hearing aids & cochlear implants similar?
Hearing aids and cochlear implants share several similarities despite their differences in technology and function:
- Improving Hearing: Both devices are designed to improve hearing abilities in individuals with hearing loss. They amplify sounds and make them easier to hear, enhancing overall auditory perception
- Assistive Devices: Both hearing aids and cochlear implants are considered assistive listening devices, providing support to individuals with hearing impairment to better communicate and engage in daily activities
- Customization: Both devices can be customized to the individual's specific hearing needs and preferences. They are available in various styles, sizes, and technology levels to accommodate different degrees and types of hearing loss
- Professional Fitting: Both hearing aids and cochlear implants require professional fitting and programming by audiologists or hearing care professionals. These specialists assess the individual's hearing profile and adjust the devices to optimize performance and comfort
- Ongoing Care: Both devices require ongoing care and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals are essential for monitoring and adjusting the devices as needed
Can you use a hearing aid with a cochlear implant?
Using a hearing aid with a cochlear implant is possible and is known as bimodal hearing. Many individuals with significant hearing loss in one ear may opt for a cochlear implant in one ear and continue using a hearing aid in the other ear. This setup allows for improved speech understanding and sound localization, as each device serves a different purpose.
However, it's essential to consult with a qualified audiologist or hearing care professional to determine the most suitable solution based on your specific hearing needs and preferences. They can provide guidance on whether bimodal hearing is appropriate for you and assist in optimizing the performance of both devices for your individual situation.
With you on your journey to better hearing.
It's time to finally treat your hearing loss. Sign up for a free consultation with a licensed hearing care professional today to determine if you have hearing loss. It’s the start of your journey towards better hearing.
EarPros benefits:
- it's 100% risk free.
- best partner with more than 1.000 stores