Ear psoriasis can cause itching, flaking and discomfort inside or around the ears. Learn what triggers it, how it differs from eczema, and which treatments — from ear drops to medical care — can help manage the symptoms.
What is ear psoriasis?
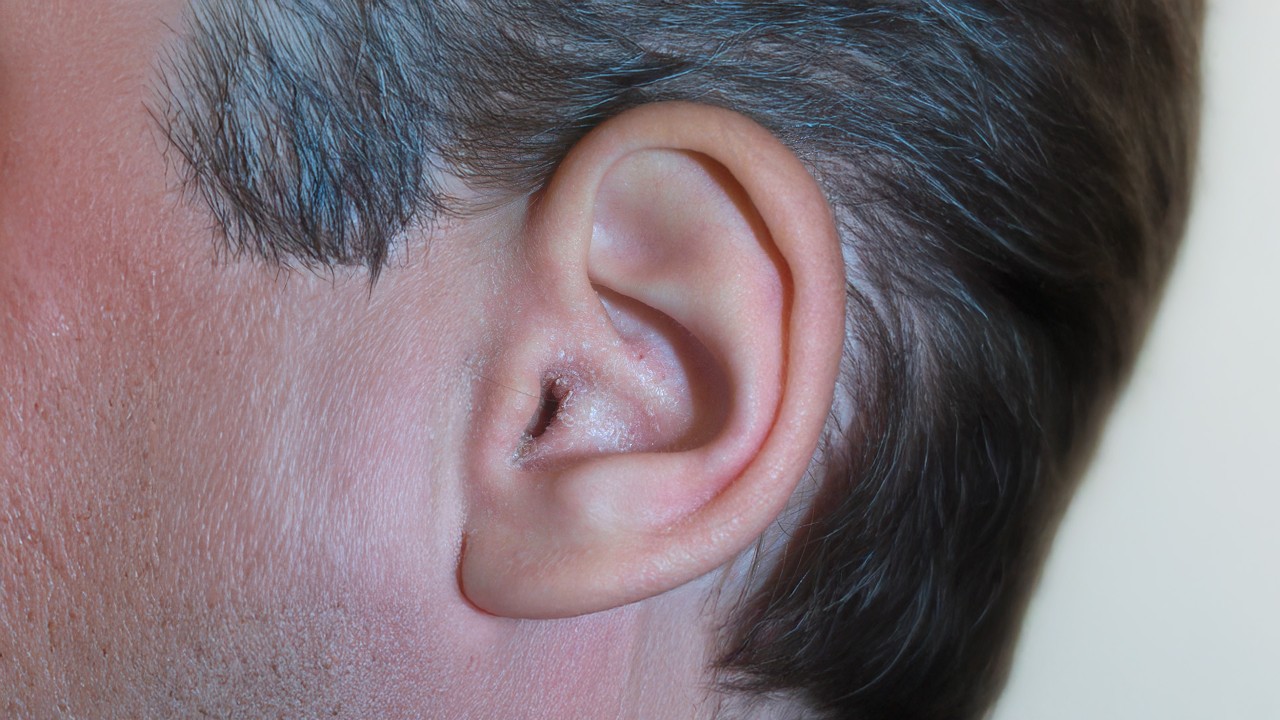
Ear psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that occurs when the immune system mistakenly accelerates the production of new skin cells. The result is a build-up of thickened, scaly skin and redness that can appear on the outer ear, inside the ear canal or behind the ear.
Although psoriasis most commonly affects the scalp, elbows, or knees, the delicate skin of the ear can also be vulnerable. The area is constantly exposed to environmental factors like humidity, temperature changes, and personal care products that can irritate already sensitive skin.
When flakes accumulate inside the ear canal, they can mix with earwax and temporarily obstruct hearing. This can cause a sensation of fullness, mild pain, or the perception that sounds are muffled. These symptoms often fluctuate depending on the severity of inflammation and whether there’s any secondary infection.
Think psoriasis might be affecting your hearing? Take the free online hearing test from EarPros to assess your hearing in minutes and get personalised insights.
Ear psoriasis: where it appears
Psoriasis can affect any part of the ear — inside the canal, on the outer ear, or behind it. Each area presents unique challenges, as the skin differs in thickness, sensitivity, and exposure to external elements. Recognising where psoriasis occurs helps you understand the symptoms and choose the most suitable treatment.
Inside the ear psoriasis
Psoriasis inside the ear canal can be difficult to manage due to the narrow, delicate skin of this region. Symptoms can range from mild itching to significant discomfort that interferes with hearing.
- Flaking and build-up of dead skin and earwax may partially block the canal, sometimes reducing hearing clarity.
- Persistent itching or fullness inside the ear often worsens in dry or humid environments.
- Subtle pain or tenderness may develop when touching the ear or using earbuds and hearing aids.
- A dry, powdery residue can appear on the outer ear when flakes migrate outward.
- Risk of irritation or infection increases if objects like cotton buds are inserted to scratch or clean.
Professional cleaning by a GP or audiologist is the safest way to remove debris and avoid eardrum damage.
Outer ear psoriasis
Psoriasis can also appear on the outer ear, including the pinna and earlobe, where skin exposure makes symptoms more visible. The condition here is often linked to scalp or facial psoriasis.
- Red, scaly patches may develop along the ear’s rim or on the earlobe, sometimes extending into the hairline.
- Dryness and cracking occur as plaques thicken, particularly in windy or cold weather.
- Itching or burning sensations may worsen with hair products, perfumes, or earrings.
- Inflamed skin folds around the outer ear can trap moisture, encouraging bacterial overgrowth.
- Mild pain or tenderness may appear when sleeping on the affected side or wearing headphones.
- Consistent moisturising and avoiding harsh cleansers help restore the skin barrier and reduce flare-ups.
Behind the ear psoriasis
Psoriasis behind the ear is one of the most common presentations and is often associated with scalp psoriasis. The area’s warmth and moisture can intensify symptoms if not properly managed.
- Red, raised plaques form behind the ear folds and may merge with scalp lesions along the hairline.
- Itchy, tight skin often causes discomfort when wearing glasses or masks with ear straps.
- Cracking or bleeding may occur in severe cases, especially if the area is frequently scratched.
- Mild infections can develop when moisture and dead skin build up in the folds.
- Gentle cleansing and fragrance-free moisturisers help soothe inflammation and maintain skin balance.
- Using medicated shampoos or topical corticosteroids prescribed by a doctor can prevent recurrence and promote healing.
Early-stage psoriasis on the ear
In its early stages, ear psoriasis often looks like small, red or pink spots covered by fine white flakes. Many people initially mistake it for dry skin or mild eczema, as the patches may not yet be thick or painful. Over time, these patches may expand, darken, and begin to itch more persistently.
Early recognition makes management easier. Moisturising the area regularly and avoiding harsh soaps or alcohol-based ear products can prevent symptoms from worsening. If you notice persistent flaking, consult a healthcare professional for a clear diagnosis — as self-treating with inappropriate creams can sometimes make psoriasis worse.
A dermatologist can examine the area using dermoscopy and, if necessary, take a small skin sample to confirm psoriasis under the microscope. This ensures that the treatment plan targets the root cause rather than the symptoms alone.


If you’re noticing persistent ear irritation, changes in hearing, or discomfort that could be linked to ear psoriasis, don’t ignore the signs. Take a proactive step to check your ear and hearing health. Find out how your ears are doing with a quick, easy online test.
Take Your FREE Online Hearing Test Today
Ear eczema vs psoriasis
Because ear eczema and psoriasis can appear similar, it’s easy to confuse the two. Both can cause redness, itching and scaling, but their underlying causes and treatment approaches differ significantly.
Eczema (also called dermatitis) often results from an overreaction to allergens, soaps, or temperature changes. It usually presents with oozing, crusting and intense itching. Psoriasis, by contrast, is an autoimmune condition where skin cells multiply too fast, creating thicker, silvery-white scales with well-defined borders.
Eczema tends to respond well to emollients and barrier-repair creams, while psoriasis often requires medicated treatments to slow down cell turnover. Because using the wrong medication can aggravate symptoms, professional diagnosis is key. A dermatologist can quickly identify the condition and guide you to safe, effective therapies.
Ear psoriasis treatment options
Managing ear psoriasis involves a combination of medical therapy, self-care and preventive habits. Treatment focuses on soothing inflammation, reducing scaling, and preventing infections or hearing issues caused by debris build-up.
Disclaimer: The information below is for educational purposes only. EarPros does not prescribe or provide medical treatment. Always consult your GP, audiologist, or dermatologist before starting any medication or therapy.
Ear psoriasis and topical medications
Topical treatments are the first line of defence for most people with ear psoriasis. These may include corticosteroid creams to reduce inflammation, vitamin D analogues (like calcipotriol) to regulate skin cell production, or salicylic acid preparations to gently remove scales.
When applied behind the ear or around the outer ear, these medications can bring noticeable relief. However, creams should never be inserted into the ear canal unless specifically prescribed for that area. Improper application can lead to irritation or infection.
Dermatologists often recommend applying topical treatments at night and using a light moisturiser during the day to maintain hydration without clogging pores.
Psoriasis ear drops
For inside ear psoriasis, specially formulated psoriasis ear drops may be prescribed. These usually contain mild corticosteroids, medicated oils, or antifungal components to relieve itching and soften scales within the ear canal.
It’s important to apply ear drops only as directed by a doctor. The dosage, frequency and duration depend on the severity of symptoms and the ear’s condition. Overuse or misuse can thin the skin and increase infection risk.
If you wear hearing aids, remove them while applying drops and allow sufficient time for the medication to absorb before reinserting them.
Phototherapy or light-based treatments
In more persistent cases, phototherapy — controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UVB) light — can slow down the excessive growth of skin cells. While it’s usually used for body and scalp psoriasis, light therapy can sometimes benefit the ear area if applied with care.
Because the ear’s skin is delicate, phototherapy should only be performed by a qualified healthcare professional. Sessions are typically short and spaced over several weeks. Many patients notice improvements in redness and scaling within a month of regular treatment.


FAQs about ear psoriasis
What causes ear psoriasis?
Can psoriasis affect hearing?
Is it safe to use ear drops for psoriasis?
How can I tell if it’s psoriasis or eczema?
With you on your journey to better hearing.
It's time to finally treat your hearing loss. Sign up for a free consultation with a licensed hearing care professional today to determine if you have hearing loss. It’s the start of your journey towards better hearing.
EarPros benefits:
- it's 100% risk free.
- best partner with more than 1.000 stores